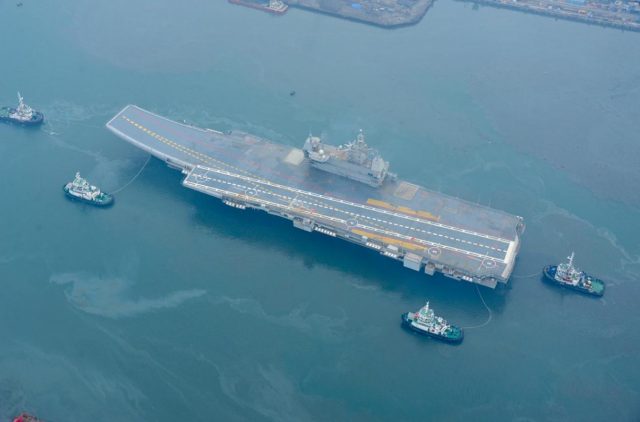
The Indian Navy’s first locally-developed aircraft carrier INS Vikrant got underway on Sunday for its third round of sea trials ahead of the ship’s planned delivery and entry into service this summer.
After testing propulsion systems and its navigational suite off the Kochi coast during its maiden sea trial in August last year, the carrier will now undertake what was termed as “complex maneuvers,” that will establish specific data on how the ship performs in various conditions.
Should all go according to plans, the carrier could be officially handed over from the Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) to the Indian Navy this spring and enter service by August.
With the commissioning, India would complete a process that started well over 12 years ago, when construction on the ship began.
Also referred to as Indigenous Aircraft Carrier (IAC), Vikrant was designed by the Indian Navy’s Directorate of Naval Design(DND).
While its commissioning is already seven years behind the original schedule, the carrier remains a cornerstone of the “Make in India” drive, which aims to boost the capacities and capabilities of the domestic defense industry. According to the Indian defense ministry, Vikrant features more than 76 percent of indigenous content.
With a length of 262 meters, and a width of 62 meters, the ship is designed for a maximum speed of 28 knots thanks to gas turbine propulsion. The crew of around 1700 people will have specialized cabins to accommodate women officers and will benefit from a high degree of automation for machinery operation, ship navigation and survivability. The ship has an endurance of about 7,500 nautical miles.
While it was designed locally by Cochin, Vikrant shares some of the design features with the current Indian Navy flagship and former Soviet carrier INS Vikramaditya, with the most obvious being the ski jump ramp that facilitates the launch of fixed-wing aircraft. India bought Vikramaditya from Russia in 2004 and commissioned it in 2013.
Once in service, INS Vikrant will operate MiG-29K fighters and Kamov-31 air early warning helicopters, as well as the locally-developed advanced light helicopters (ALH).
Additionally, India is currently in the process of assessing the suitability of the naval version of the French Rafale fighter for operations from INS Vikrant. Starting this month, Rafale-M aircraft are slated to undergo flight tests at the ground test facility at the INS Hansa base in Goa.