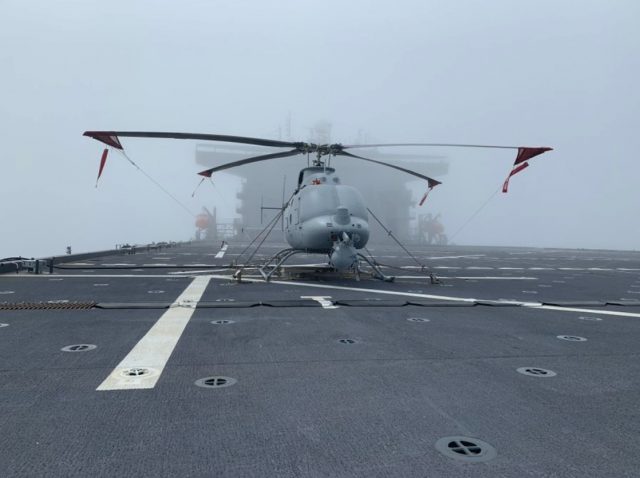
The US Navy’s MQ-8C Fire Scout unmanned helicopter has completed dynamic interface testing aboard the expeditionary sea base ship USS Hershel “Woody” Williams.
The US Naval Air Systems Command announced the milestone on April 12, without revealing when the testing was completed.
Dynamic interface testing involves validating and expanding the general launch and recovery envelope relative to “winds over deck” for the ship’s helicopter spots. The tests are used to demonstrate the future concept of operations for unmanned helicopters aboard the ship. This phase of testing usually precedes the operational evaluation phase.
USS Hershel “Woody” Williams (ESB 4), a special operations support ship capable of landing V-22 and MH-53E equivalent helicopters and unmanned systems, entered service in Norfolk, Virginia, on March 7.
Named after Marine Corps Chief Warrant Officer Four Hershel Woodrow Williams, ESB 4 is the fourth ship in its class.
The 239-meter ships are capable of facilitating missions ranging from airborne mine countermeasures operations to special operations forces support. Featuring a four spot flight deck, mission deck and hangar, the ships are designed around four core capabilities: aviation facilities, berthing, equipment staging support and command and control assets.
The MQ-8C Fire Scout is an unmanned helicopter built by Northrop Grumman on the basis of the Bell 407 single-engine helicopter. Developed specifically for the US Navy, the Fire Scout is designed to provide reconnaissance, situational awareness, aerial fire support and precision targeting support for ground, air and sea forces. It achieved initial operational capability in June 2019. The system has a range of 150 nautical miles and a payload capacity of more than 700 pounds.