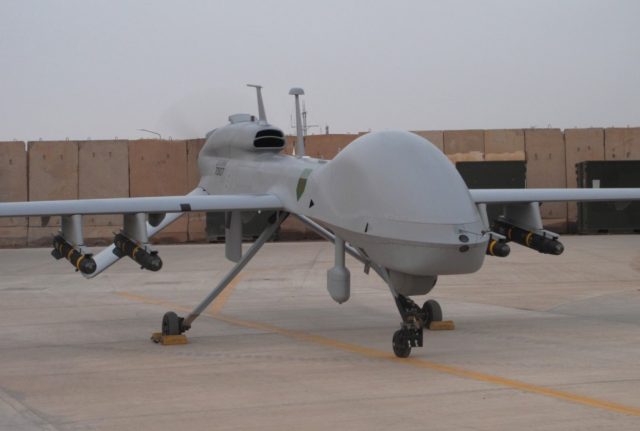
The US Air National Guard Air Force Reserve Command Test Center (AATC) recently completed a test launch of the new AGM-114 R-4 Hellfire missile from an MQ-9 Reaper drone.
The test of the modified Hellfire missile, which can fly roughly three times as far as previous versions, was carried out as part of the Valiant Shield exercise that took place this summer.
During the exercise, AATC led the successful test of the AGM-114 R-4 and the associated weaponeering software. According to AATC, the launch resulted in the longest Hellfire shot taken to date.
It also demonstrated the AGM-114 R-4’s ability to double the MQ-9’s standoff range, giving the ability to engage threats while maintaining a safe distance out of the threats ability to counter-strike, which is crucial to survivability in a contested environment.
The AGM-114 Hellfire family of missiles includes the Hellfire II and Longbow Hellfire missiles. The missile is a precision strike, semi-active laser (SAL) guided air-to-ground weapon for US Army’s AH-64 Apache, OH-58 Kiowa Warrior, Reapers, US Marine Corps AH-1W Super Cobras, and US Air Force’s Predator/Reaper UAS.
The AGM-114R (R standing for Romeo), which is designed to replace all other missile variants, has a stated range of up to 8 kilometers, which means the modified R-4 missile that was tested could provide Reapers with the capability to strike targets at ranges of around 24 kilometers.
It is worth noting that US Air Force has worked on a software tweak that will allow the Reaper to carry eight live AGM-114 Hellfire missiles for the drone’s “persistent attack” role.
For the Valiant Shield trial, the AATC MQ-9 Test Detachment was supported by the 174th Attack Wing with Block 5 MQ-9 aircraft. The 556th Test and Evaluation squadron supported with a block 30 Ground Control Station, while test flights were flown out of Creech AFB using Air Combat Command (ACC), Air National Guard (ANG) and Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC) aircrew.
AATC is a MAJOM Operational Test Organization chartered to test aircraft modernization efforts and the ARC’s Battlefield Airman Enterprise which includes Intelligence, Surveillance, & Reconnaissance, Cyber, Space, and all other Combined Test Forces.