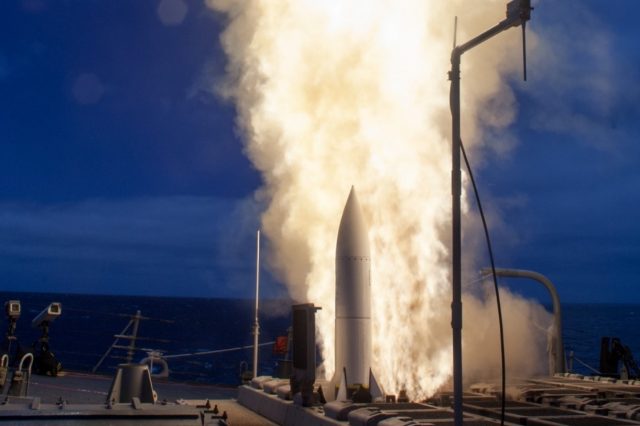
South Korea’s Defense Project Promotion Committee gave its green light on Tuesday for the country’s purchase of Standard Missile-6 (SM-6) interceptors from the United States.
The body approved 760 billion won (US$606 million) for the procurement project that would see the Republic of Korea Navy field the Raytheon-built missile.
More specifically, the missiles would be installed on the ROK Navy’s KDX-III destroyers. It is unclear whether the SM-6 would be employed by the three Batch I destroyers (also known as Sejong the Great-class) currently in service, or the second batch of ships that is currently under construction.
A new generation of South Korean destroyers that would be built after the KDX-III ships was expected to deliver a smaller design, but with exclusively Korean weapon systems and sensors.
The country announced its decision to procure the SM-6, a dual-capability missile that can be used for either air defense or ballistic missile defense, amid increased North Korean missile test activity. Since the start of the year, North Korea has completed at least 13 launches, including the first intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) test since 2017, as well as the launch of a new guided weapon designed “to improve tactical nuclear operations.”
South Korea’s Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA) expects to complete the purchase of missiles through a government-to-government agreement by 2031.
Raytheon touts the SM-6 as “three missiles in one,” saying it is the only weapon that can perform anti-air warfare, ballistic missile defense and anti-surface warfare missions. Propelled by a solid rocket booster and a dual thrust solid rocket motor, the 1.5-ton missile has a range of close to 500 kilometers. In service with the US Navy, the SM-6 completed development and achieved initial operational capability in November 2013.