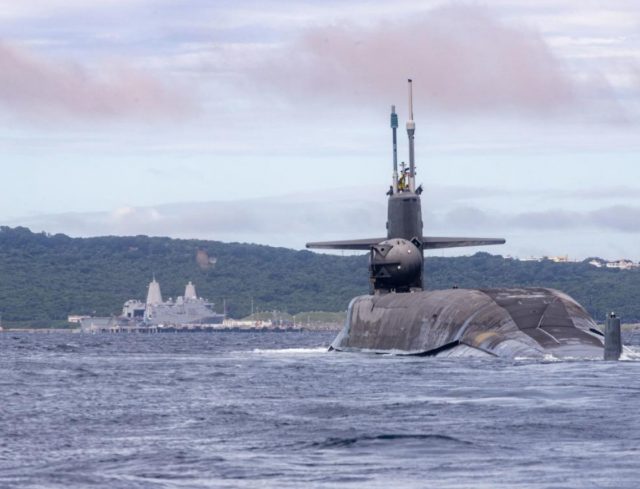
US Navy Ohio-class guided-missile submarine USS Michigan (SSGN 727) made a brief stop for personnel near Okinawa, Japan earlier this month as part of her deployment to the US 7th Fleet area of operations.
Based out of Naval Base Kitsap in Washington, the submarine is operating in the US 7th Fleet under the command and control of Commander, Task Force 74, the Navy said in the latest in a series of submarine operations disclosures this year.
While the movement of a guided-missile submarine (SSGN) is usually not so secretive as the operations of a ballistic missile (SSBN) one, the rate of official announcements on their operations is unusual.
Earlier this month, the US Navy announced SSBN USS Rhode Island was on a rarely-made port visit to the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The Rhode Island announcement followed the disclosure of the location of another SSBN, USS West Virginia, which was operating in the Arabian Sea at the time of the visit of US Central Command head to the submarine.
“Having Michigan in theater adds to our already deep bench of undersea warfare capabilities throughout the region,” said Rear Adm. Rick Seif, Commander, Submarine Group 7. “Their presence demonstrates our continued commitment to providing maritime security and deterrence in the Indo-Pacific.”
Michigan was commissioned on Sept. 11, 1982. It is the second submarine of the Ohio-class of ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs) and SSGNs, and the third US Navy ship to bear the name.
The 40-year-old submarine is now operating in the Asia Pacific after completing an 18-month dry dock refit period in March 2021, which allowed her to put in a few more years of service before retiring.
Michigan was built to carry the Navy’s third generation submarine-launched ballistic missile, the Trident C-4. After arriving in Bangor in March 1983, Michigan would carry out her primary mission of deterrence for nearly 20 years, conducting more than 60 strategic deterrent patrols.
At the conclusion of the Cold War, Michigan, Ohio and two sister ships – USS Florida (SSBN 728) and USS Georgia (SSBN 729) – were considered for decommissioning. Instead, the Navy chose to convert the Ohio-class seaframe to carry Tomahawk land attack missiles or other payloads in lieu of ballistic missiles.
Ohio-Class guided-missile submarines (SSGN) provide the Navy with unprecedented strike and special operation mission capabilities from a stealth, clandestine platform. Armed with tactical missiles and equipped with superior communications capabilities, SSGNs are capable of directly supporting combatant commander’s strike and special operation forces requirements.